Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease refers to the buildup of excess fat in liver cells, which can lead to inflammation, liver damage, and potentially liver cirrhosis. There are two kinds of fatty liver disease: Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD), which is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), which is more common and is associated with obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD can progress to a more severe condition known as Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), characterized by inflammation and may lead to liver scarring and failure.
Causes and Risk Factors of NAFLD
NAFLD is rooted in various risk factors, including:
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases fat accumulation in the liver.
- Diabetes: Insulin resistance contributes to fat buildup in liver cells.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of fats in the blood can lead to fatty liver.
- Poor Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of developing NAFLD.
- Genetics: Family history plays a role in susceptibility to liver diseases.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Many individuals with NAFLD may not experience noticeable symptoms in the early stages. As the disease progresses, potential symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort or pain (especially in the upper right abdomen)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Weakness
- Swelling in the abdomen
- Enlarged liver
Due to the often silent nature of NAFLD, regular check-ups and liver function tests are essential for early detection.
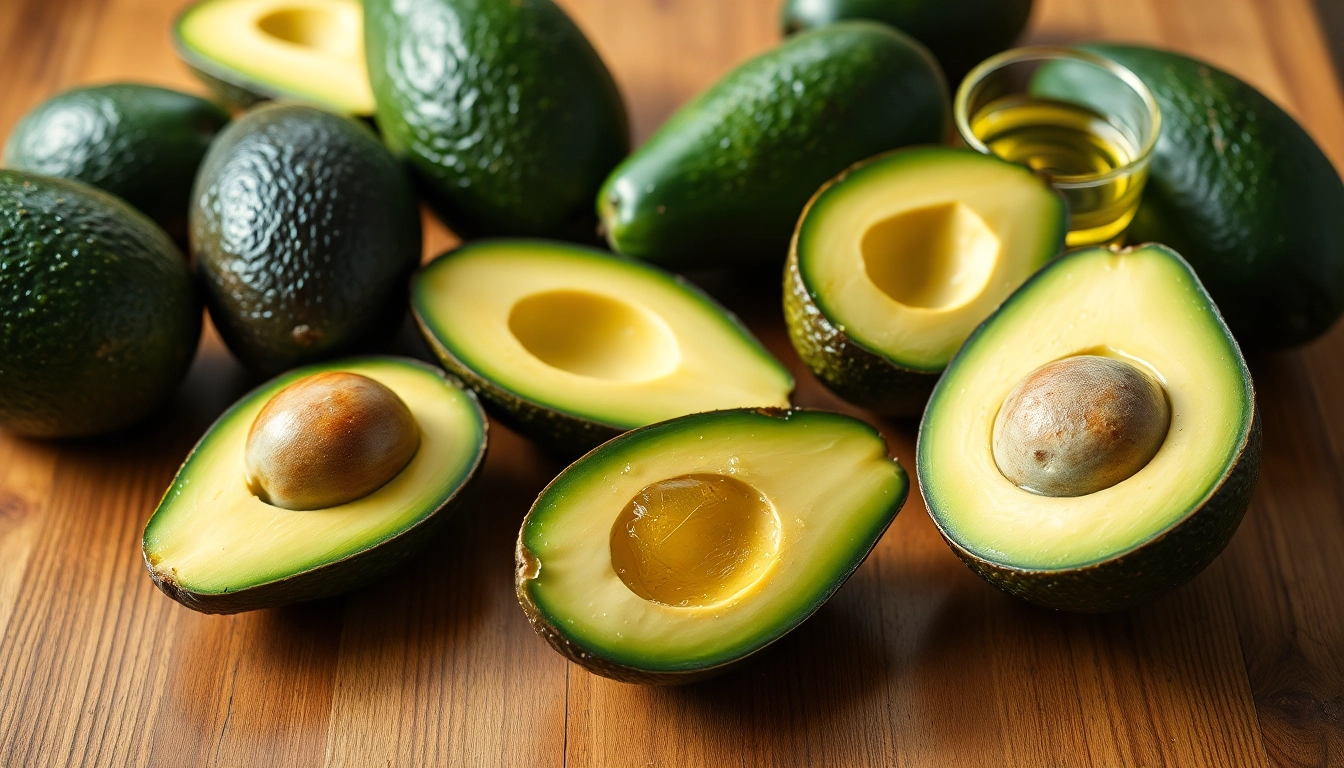
Benefits of Avocado for Liver Health
Nutritional Profile of Avocados
Avocados are rich in vital nutrients and compounds known to be beneficial for overall health. A single avocado (approximately 200 grams) contains:
- Calories: 320
- Monounsaturated Fat: 15 grams
- Fiber: 13 grams
- Vitamin K: 25% of the RDA
- Folate: 20% of the RDA
- Vitamin C: 17% of the RDA
- Potassium: 14% of the RDA
These nutrients, particularly healthy fat and fiber, contribute to improved heart and liver health.
How Avocados Influence Liver Function
Research has shown that the monounsaturated fats in avocados can play a pivotal role in supporting liver health. These fats help reduce levels of harmful lipids in the bloodstream, which is significant for individuals with NAFLD. By decreasing lipid accumulation in the liver, avocados may help prevent further liver damage.
Additionally, avocados contain antioxidants, such as glutathione, which assists in detoxifying the liver and combating oxidative stress—both crucial in managing liver health.
Scientific Studies on Avocado and Liver Health
Various studies have examined the impact of avocado on liver health:
- A 2015 study highlighted in *Healthline* reported that avocado extract may serve as a protective agent against liver damage, showing some promise in lowering blood lipid levels and mitigating metabolic syndrome effects.
- Recent research published in the *Journal of Food Science and Technology* concluded that avocado oil could enhance liver function by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation, essential factors in NAFLD progression.
- Conversely, some studies caution against excessive avocado consumption, suggesting that “good fats” can still contribute to fatty liver if abused, emphasizing moderation.
Incorporating Avocado Into Your Diet
Healthy Recipes with Avocado
There are numerous tasty and nutritious ways to incorporate avocados into daily meals:
- Avocado Toast: Spread mashed avocado on whole grain toast, topped with poached eggs, tomatoes, and a sprinkle of salt and pepper.
- Guacamole: Mash avocados with lime juice, cilantro, diced tomatoes, and onions for a healthy dip or condiment.
- Salads: Add cubed avocado to salads for a creamy texture; they pair well with leafy greens, beans, and nuts.
- Smoothies: Blend avocados into smoothies along with fruits such as bananas and spinach for a nutrient-dense drink.
Portion Control and Serving Suggestions
While avocados are healthy, it’s essential to practice portion control. A serving size is typically 1/3 to 1/2 of an avocado. Large avocados can be calorie-dense, so pairing them with other nutrient-rich foods minimizes overall caloric intake while maximizing health benefits. Here are some serving suggestions:
- Combine with lean proteins like grilled chicken or fish.
- Mix into oatmeal for a unique texture and flavor.
- Use as a spread on sandwiches instead of butter or margarine.
Combining Avocado with Other Liver-Friendly Foods
Incorporating avocados into a balanced diet can promote liver health effectively. Pairing avocados with foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon or walnuts, can be beneficial. Also, mixing avocados with high-fiber foods like beans, legumes, and whole grains aids in the control of blood sugar levels and promotes satiety.
Myths and Misconceptions About Avocados
Good Fats vs. Bad Fats: What to Know
One prevalent myth is that all fats, including those from avocados, are detrimental to health. In reality, the monounsaturated fats found in avocados are considered “good fats.” They play a crucial role in heart health, promoting healthy cholesterol levels while reducing inflammation. However, because these fats are still calorie-dense, moderation is key.
Common Misunderstandings Regarding Avocado Consumption
Many people restrict avocados due to their high fat content, misunderstanding their nutritional benefits. Avocados contribute to satiety and can help regulate weight when consumed as part of a balanced diet. It’s important to understand that the quality of fat matters, and choosing foods with beneficial fat profiles can aid in the prevention of NAFLD.
Research Insights on Avocados and Liver Health Risks
The concern over excessive avocado consumption stems from studies suggesting it can lead to unhealthy fat deposition. Thus, while avocados are beneficial, moderate consumption is advisable. A diverse diet focusing on whole foods, combined with avocados, provides an optimal approach to minimizing liver health risks.
Conclusion: Avocados as a Healthful Choice
Summary of Key Benefits
In summary, avocados offer a multitude of health benefits: they are nutrient-rich, help regulate blood lipids, and provide necessary fats that can aid in maintaining liver health. When incorporated into a balanced diet, they can help manage and potentially reverse conditions like NAFLD.
Final Thoughts on Dieting for Liver Health
For individuals at risk of fatty liver disease, making informed food choices is paramount. Avocados can be a valuable addition to the diet when prepared without excessive unhealthy fats or sugars. Incorporating them mindfully is essential for overall liver health.
Encouragement for Healthy Lifestyle Changes
Incorporating avocado and fatty liver-friendly choices into your diet is just one part of a healthy lifestyle. Regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol intake are vital components in managing liver health. Empowering yourself with knowledge about nutritional choices and actively monitoring your lifestyle can lead to better long-term health outcomes.