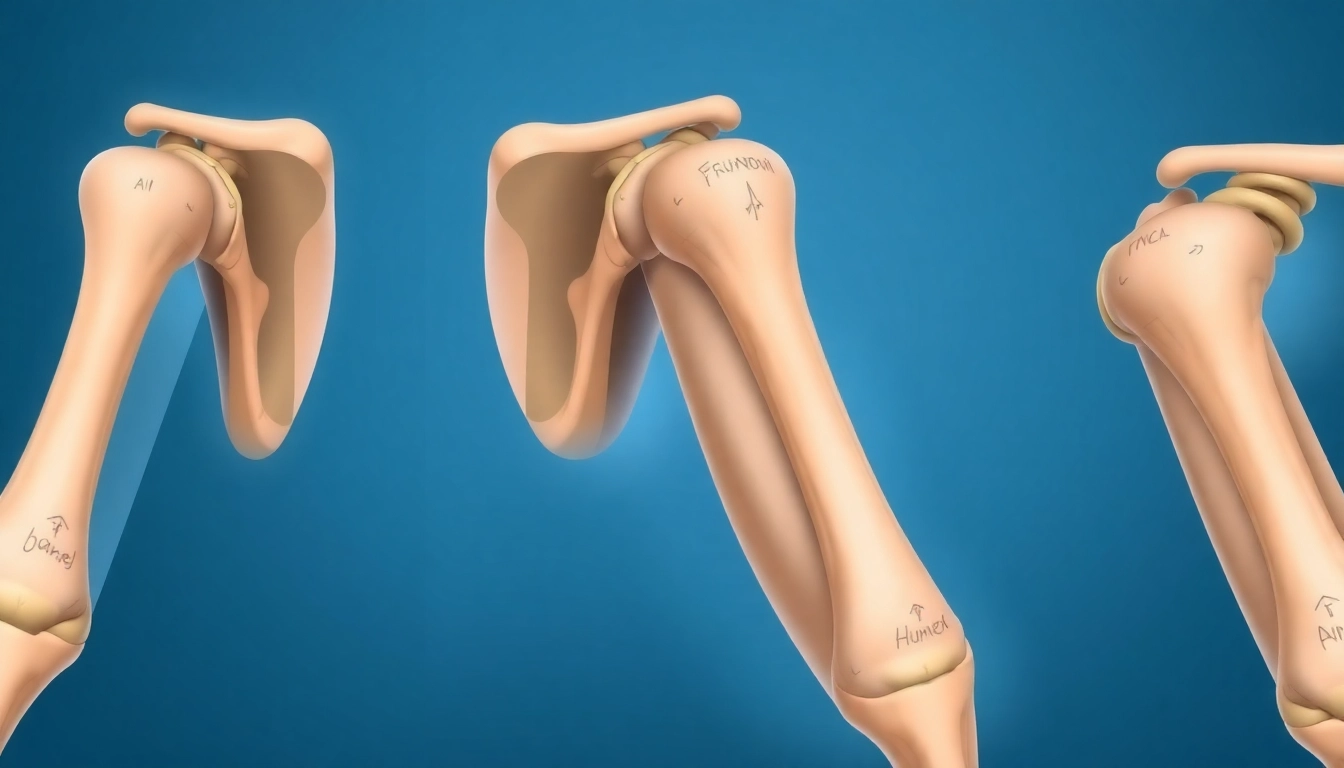
Understanding Types of Humerus Fracture
The humerus is an integral bone in the human upper limb, serving as the main structural unit of the arm. Fractures of this bone are essential to understand, especially in clinical settings. There are various types of humerus fractures that differentiate by their location and cause, which can critically influence treatment and recovery. By familiarizing yourself with the types of humerus fracture, you can gain insights into their implications for mobility and overall health.
What Is the Humerus?
The humerus is the long bone that runs from the shoulder to the elbow, forming the upper arm. Its structure comprises three main sections: the proximal humerus, which is situated near the shoulder; the mid-shaft, which constitutes the length of the bone; and the distal humerus, located near the elbow. The humerus plays a crucial role in facilitating arm movements, stability, and strength while connecting with the shoulder joint and the elbow.
Common Causes of Humerus Fractures
Humerus fractures can occur due to various mechanisms, including:
- Trauma: Falls, particularly in older adults, are a leading cause. Young individuals may face fractures from sports injuries.
- Direct Impact: Accidents involving vehicles or blows to the arm can lead to severe fractures.
- Pathological Causes: Conditions such as osteoporosis weaken bones, making them more susceptible to fractures.
Classification of Humerus Fractures
Fractures of the humerus can be classified based on their location:
- Proximal Humerus Fracture: Occurs near the shoulder joint.
- Humerus Shaft Fracture: Takes place in the mid-section of the bone.
- Distal Humerus Fracture: Happens near the elbow joint.
Each of these classifications has distinct characteristics that can influence management and recovery options.
Proximal Humerus Fracture Explained
Definition and Anatomy
A proximal humerus fracture refers to a break occurring at the upper part of the humerus, near the shoulder joint. It can involve various anatomical structures, including the greater and lesser tuberosities and the humeral head. These fractures are prevalent in older adults, especially those with osteoporosis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Patients with proximal humerus fractures typically exhibit symptoms such as:
- Pain and tenderness around the shoulder
- Swelling and bruising
- Restricted movement in the shoulder joint
Diagnosis is primarily conducted through physical examinations and imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, to assess the type and extent of the fracture.
Treatment Options
Treatment for proximal humerus fractures can vary based on the fracture type and patient age:
- Non-Surgical Management: For stable fractures, treatment may include immobilization with a sling, pain management, and physical therapy.
- Surgical Options: In cases of significant displacement or comminuted fractures, surgical interventions may be required, such as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), or shoulder replacement surgery.
Mid-Shaft Humerus Fracture: Key Insights
Understanding Mid-Shaft Fractures
Mid-shaft humeral fractures occur in the central part of the bone and can result from high-energy trauma, such as sports injuries or falls. They tend to disrupt the surrounding soft tissue and may involve damage to the radial nerve, which can affect wrist and finger movements.
Diagnosis and Symptoms
Mid-shaft fractures display distinct symptoms:
- Severe pain in the arm
- Deformity or unnatural angulation of the arm
- Inability to move the arm
Diagnosis typically involves thorough physical exams and imaging studies. An X-ray can often show the fracture type and alignment.
Management and Recovery
Management strategies for mid-shaft fractures include:
- Conservative Treatment: In cases where the fracture is stable, conservative measures that include a cast or splint may be adequate.
- Surgical Intervention: They may require surgery if the fracture is displaced or involves compromised blood flow to the surrounding area. Techniques might involve intramedullary nailing or plating.
Recovery time can take several months, during which physical therapy is crucial for regaining strength and functionality.
Distal Humerus Fracture: What You Need to Know
Characteristics of Distal Fractures
Distal humerus fractures occur at the lower end of the humerus, near the elbow joint. They can happen due to falls, direct hand impacts, or in individuals with weakened bones. These fractures often result in complications affecting elbow joint function.
Signs and Diagnostic Methods
Signs of a distal humerus fracture include:
- Intense pain in the elbow
- Swelling and inflammation around the joint
- Limited range of motion
Diagnosis may involve physical exams and imaging, including X-rays and MRI scans, to ascertain the fracture’s nature and plan for treatment.
Overview of Treatment Strategies
Treatment for distal humerus fractures can be complex due to the intricate anatomy around the elbow. Options may include:
- Non-Operative Methods: Minor fractures can often be treated with splinting, physical therapy, and close follow-up.
- Operative Techniques: More severe fractures may necessitate surgical interventions such as ORIF with plates or screws to restore elbow alignment and stability.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Humerus Fractures
Initial Recovery Phase
The first stage of recovery involves immobilization to ensure proper bone healing. Pain management, rest, and gradual passive movements are vital. The duration can vary from weeks to months depending on the fracture severity and location.
Physical Therapy Advances
Physical therapy plays an integral role in rehabilitation. Therapists typically introduce exercises focusing on:
- Restoring range of motion
- Enhancing strength through resistance training
- Incorporating functional activities to ensure a return to normal life
Personalized physical therapy plans can significantly impact long-term recovery and function.
Long-Term Effects and Care
Some individuals may experience long-term effects, including chronic pain, stiffness, or reduced functionality. Ongoing outpatient therapy or lifestyle adjustments can aid recovery. Regular follow-up appointments with orthopedists can help monitor healing and address any arising issues.