1. Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
1.1 What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease is a condition characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells. When more than 5% to 10% of the liver’s weight is made up of fat, it is deemed fatty liver disease (FLD). There are two main types: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which occurs in people who drink little or no alcohol, and alcoholic liver disease (ALD). Fatty liver is often asymptomatic but can lead to more serious liver-related health issues if left unchecked.
1.2 Causes and Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. These include:
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly fat around the abdomen, is a primary risk factor.
- Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance increase the risk of NAFLD.
- Lipid Disorders: High levels of triglycerides and low levels of HDL cholesterol are commonly associated with fatty liver.
- Metabolic Syndrome: This syndrome, which includes factors like obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, increases the chances of NAFLD.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles significantly raise the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
1.3 Symptoms and Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
Most individuals with fatty liver disease do not experience symptoms, especially in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, common symptoms may include:
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen
- Weight loss without trying
- Jaundice (in advanced cases)
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to check liver function, imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to assess liver fat content, and occasionally, a liver biopsy to evaluate the degree of inflammation and damage.
2. The Role of Diet in Liver Health
2.1 Importance of Healthy Fats in Your Diet
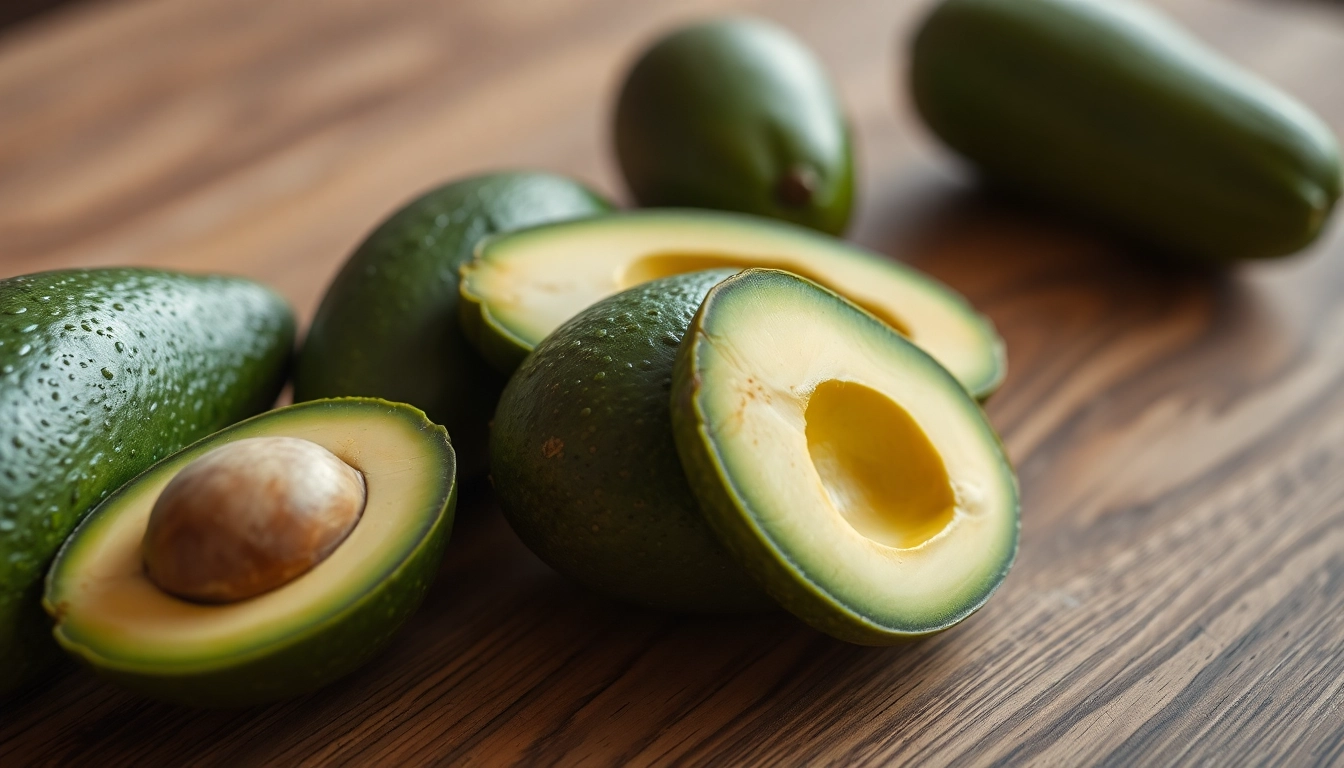
Diet plays a crucial role in liver health, especially when it comes to fat consumption. Healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are vital for maintaining proper liver function and aiding in the prevention and management of fatty liver disease. Monounsaturated fats—found in foods like avocados and olive oil—have been shown to reduce liver fat and improve markers of liver health.
2.2 Foods Beneficial for Fatty Liver
Incorporating certain foods into the diet can significantly benefit liver health:
- Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, helping reduce liver fat.
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and trout are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial in reducing liver fat and inflammation.
- Nuts: Walnuts and almonds contain healthy fats and antioxidants that support liver function.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Leafy greens, berries, and citrus fruits provide essential vitamins and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oatmeal, and whole grain bread are high in fiber, which helps improve liver health.
2.3 Foods to Avoid for Liver Health
On the other hand, certain foods can exacerbate liver issues and should be minimized or avoided:
- Sugar and Sugary Beverages: High sugar intake can contribute to fat accumulation in the liver.
- Trans Fats: Highly processed foods and baked goods containing trans fats can worsen liver fat.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread and pasta can lead to increased fat storage in the liver.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption is a leading cause of liver disease, and for those with fatty liver, it should be avoided.
3. Nutritional Benefits of Avocado
3.1 Avocado’s Healthy Fats and Their Impact on Lipids
Avocados are often hailed as a superfood for their high content of healthy fats, specifically monounsaturated fatty acids. These fats are known to lower bad LDL cholesterol levels while increasing good HDL cholesterol levels. Research indicates that incorporating avocados into the diet can improve lipid profiles and, consequently, liver health. A 2015 study reported that avocado may help lower blood lipids and prevent liver damage in individuals diagnosed with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
3.2 Antioxidant Properties of Avocados for Liver Health
In addition to healthy fats, avocados are rich in antioxidants such as vitamin E, glutathione, and carotenoids. These compounds help combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation in liver tissues. The presence of antioxidants can play a significant role in supporting liver detoxification processes, ultimately contributing to improved liver health.
3.3 How Avocado Can Aid in Liver Detoxification
Avocados are known for their ability to facilitate liver detoxification, largely due to their high levels of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that protects liver cells from damage. This detoxification process can help clear out harmful substances, fats, and toxins from the liver. Integrating avocado into your diet can support these functions and potentially reverse early stages of fatty liver disease. For more information on how a balanced diet can help with liver health, refer to our article on avocado fatty liver.
4. Incorporating Avocado into Your Diet
4.1 Delicious Avocado Recipes for Liver Support
Getting creative with avocados can not only enhance your meals but also support liver health. Here are a few delicious recipes:
- Avocado Salad: Combine diced avocado, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, and a sprinkle of feta cheese with a drizzle of olive oil and lemon juice.
- Avocado Toast: Spread mashed avocado on whole-grain bread, topped with a poached egg and chili flakes for extra flavor.
- Avocado Smoothie: Blend ripe avocado with spinach, banana, yogurt, and almond milk for a nutritious morning beverage.
- Guacamole: Mash avocado with fresh lime juice, garlic, salt, and chopped cilantro for a tasty dip that’s rich in healthy fats.
4.2 Tips for Including Avocados in Daily Meals
Incorporating avocados into your meals can be simple and straightforward. Here are some tips:
- Slice avocados into salads for added creaminess and nutrition.
- Add avocado to sandwiches or wraps as a substitute for mayonnaise or butter.
- Use avocado oil for cooking or as a dressing for salads.
- Experiment with adding avocado to desserts, such as smoothies or chocolate mousse, to boost healthy fats.
4.3 Portion Control: How Much is Too Much?
While avocados are highly nutritious, portion control is essential. A typical serving is about one-third to one-half of a medium avocado. Consuming too much can lead to excessive calorie intake, potentially contributing to weight gain. Balancing your avocado intake with other fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats ensures you receive a wide range of nutrients without overindulging.
5. Lifestyle Changes for Fatty Liver Management
5.1 The Importance of Regular Exercise
Exercise plays a critical role in managing fatty liver disease. Regular physical activity aids in weight loss, improves insulin sensitivity, and helps lower liver fat levels. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, such as brisk walking or cycling, can drastically improve liver function and overall health.
5.2 Hydration and Its Role in Liver Health
Staying hydrated is crucial for liver health. Water helps the liver flush out toxins and process nutrients effectively. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water a day, and consider herbal teas like dandelion or green tea, which are also beneficial for liver detoxification.
5.3 Regular Check-ups and Monitoring Liver Health
For individuals at risk of fatty liver disease, regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential. Blood tests, imaging, and, if necessary, liver biopsy can help monitor liver health. Early detection of any issues allows for timely intervention and lifestyle adjustments to prevent further deterioration of liver function.